|
|
- pronunciation:
- ae
j
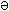 teIt
teIt
- parts of speech:
- transitive verb, intransitive verb
- features:
- Word Combinations (verb), Word Explorer, Word Parts
| part of speech: |
transitive verb |
| inflections: |
agitates, agitating, agitated |
| definition 1: |
to cause to move briskly or with force.
A washing machine works by agitating the clothes.The wind agitated the curtains.- synonyms:
- churn, shake
- similar words:
- convulse, jiggle, ruffle, toss, trouble, vibrate
|
| definition 2: |
to upset or excite, esp. emotionally.
His indifference agitated me.
- synonyms:
- disturb, excite, fluster, ignite, inflame, perturb, rile, rock, roil, shake, shock, trouble, unsettle, upset
- antonyms:
- calm, compose, lull, soothe, still, tranquilize
- similar words:
- alarm, bother, discompose, disorder, disquiet, distract, exercise, flurry, instigate, jar, provoke, rattle, ruffle, stir, work up
|
| related words: |
affect, anger, churn, dismay, disturb, enrage, fan, fluster, frenzy, fret, frighten, incense, incite, inflame, jangle, madden, outrage, rile, rock, rouse, shake, startle, thrill, trouble, wake, warm, whip, wind up, worry |
|
|
| part of speech: |
intransitive verb |
| definition: |
to arouse, or attempt to arouse, public support (often fol. by "for" or "against").
Feminists agitate for women's rights.Protesters agitated against the building of a nuclear power plant in the area.- similar words:
- advance, argue for, foment, incite, instigate, promote, provoke
|
| related words: |
demonstrate |
adverb + (v.)agitate
bit,
clearly,
constantly,
continually,
deeply,
easily,
extremely,
gently,
greatly,
highly,
increasingly,
merely,
noticeably,
obviously,
particularly,
severely,
somewhat,
strangely,
vigorously,
violently,
visibly
[See all][See only the most frequent]
(v.)agitate
+ noun
autonomy, cause, change, independence, injustice, minute, nurse, pile, reform, soul, stand
|
| derivations: |
agitated (adj.), agitatedly (adv.) |
The word agitate
contains the following parts:
act, ag
Latin
root
that means do, drive
  Example words:
action, activate, active, actively, activist, activity, actor, actress, actual, agency, agenda, agent, agile, agitate, enact, hyperactive, interact, interaction, interactive, radioactive, react, reaction, reactor, reagent, retroactive, transact, transaction
-ate1
Latin
verb-forming suffix
that means to make, cause, do
  More about this word part:
The suffix -ate
primarily forms transitive verbs from Latin bases. Many -ate
verbs were loanwords from Latin. Verbs ending in -ate
combine with the suffix -ion to form nouns ending in -ation. These verbs also have corresponding agent nouns ending in -ator (navigator, dictator, elevator).
  Example words:
abbreviate, abdicate, abnegate, accelerate, accommodate, accumulate, activate, adequate, adjudicate, administrate, administrative, administrator, advocate, aerate, affiliate, agglomerate, agglutinate, aggravate, agitate, alienate, allocate, alternate, animate, annihilate, annotate, arrogate, aspirate, assimilate, associate, calibrate, capitulate, cerebrate, circulate, collaborate, collocate, commemorate, complicate, concentrate, congregate, consecrate, consummate, cooperate, coordinate, decapitate, decelerate, decerebrate, decimate, dedicate, dehydrate, deliberate, derogate, desecrate, dictate, disintegrate, dislocate, dissimulate, dissociate, divagate, domesticate, dominate, donate, duplicate, educate, elaborate, elevate, elongate, elucidate, emasculate, emigrate, enervate, enunciate, equate, equivocate, eradicate, evacuate, exasperate, exfoliate, expurgate, fluctuate, formulate, generate, gradate, graduate, gyrate, illuminate, illustrate, implicate, incorporate, indoctrinate, innovate, interpellate, interrogate, irradiate, irrigate, legislate, liberate, locate, mediate, motivate, narrate, navigate, negate, nominate, obliterate, operate, orate, originate, ovulate, palpate, participate, placate, populate, prognosticate, proliferate, radiate, regulate, resonate, rotate, segregate, simulate, subjugate, terminate, vacate, validate, contraindicate
|